Multitube Heat Exchanger: Superior Heat Transfer
Menu
Latest News
Product introduction
Multitube heat exchanger introduction
A multi-tube heat exchanger, also known as a tubular heat exchanger, is a high-efficiency heat exchange device that transfers heat between different fluids through heat transfer tubes in a cylindrical shell. It is suitable for high temperature and high pressure environments and can meet the heat exchange needs of various industrial fluids.
Multi-tube heat exchanger composition
The multi-tube heat exchanger is mainly composed of the following components:
1. Shell: as an external structure, it is generally cylindrical and contains heat transfer tubes inside.
2. Heat transfer tube bundle: located in the shell, both ends are fixed in the tube plate, is the core component of heat exchange.
3. Tube plate: located at both ends of the shell, it is used to fix the tube bundle and ensure tightness to prevent fluid mixing.
4. Baffle (baffle) : installed in the shell, guide shell flow through the tube bundle several times, enhance turbulence, improve heat transfer efficiency.
5. Pipe box: connected to both ends of the heat exchanger, connected to the tube plate, responsible for distributing and collecting pipe flow.
Multi-tube heat exchanger features
Advantages of multi-tube heat exchangers include:
1. High heat transfer coefficient: The use of high thermal conductivity materials such as copper or stainless steel made of threaded pipes, the design of the formation of strong turbulence, improve heat transfer efficiency.
2. Compact structure: large heat transfer area per unit volume, saving materials and space.
3. Anti-scaling ability: special threaded pipe design and thermal expansion reduce impurity attachment and extend service life.
4. Leak-proof design: Short sealing circumference and compensating thread design reduce leakage risk.
5. Wide applicability: A variety of models to meet different process needs, such as fixed tube plate, floating head type, U-shaped tube type, etc.
6. Easy maintenance: part of the design supports tube bundle disassembly, easy cleaning and maintenance.
Multi-tube heat exchanger application field
- Chemical industry: heating and cooling of raw materials or products to support chemical reactions.
- Oil and natural gas: high-temperature and high-pressure heat exchange in the refining process.
- Food processing: heating, cooling and pasteurization to ensure food safety and quality.
- Power industry: Steam generation and condensation, key equipment for power stations.
- Metallurgical industry: heat treatment furnace temperature control and metal product cooling.
- HVAC: Hot water heating and cooling in heating and air conditioning systems to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature.
Technical principle of
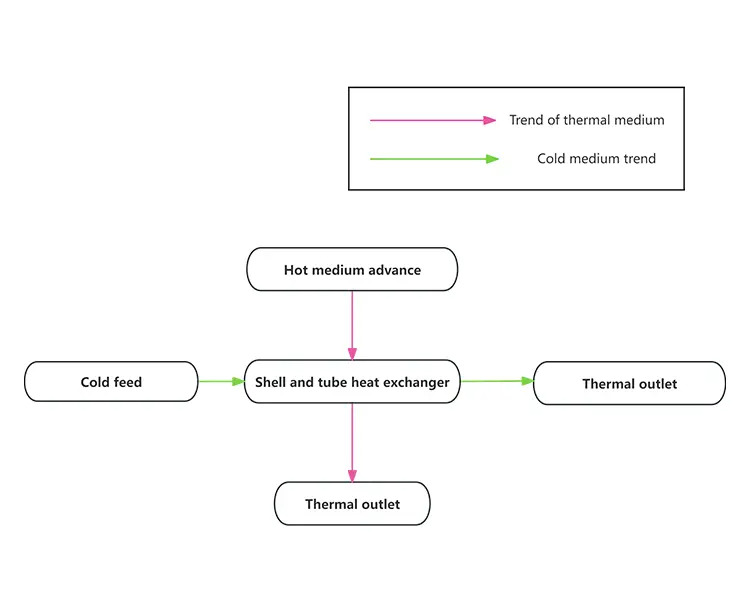
The technical principle of shell and tube heat exchanger is mainly based on wall heat transfer, in which a fluid flows inside the tube bundle, and another fluid flows in the shell outside the tube bundle, and the two exchange heat through the tube wall. Specifically, the working principle of shell and tube heat exchanger includes the following aspects:
1. Heat transfer surface: the wall of the tube bundle is used as a heat transfer surface, and two kinds of working fluids flow inside and outside the tube respectively, and heat exchange through the tube wall.
2. Fluid flow: pipe flow in the tube, shell flow outside the tube. In order to improve the heat transfer efficiency of the pipeline fluid, some designs use spiral tubes or nodule tubes, which can increase the degree of turbulence of the fluid, thereby improving the heat transfer coefficient.
3. Temperature control: By adjusting the heat source flow into the heat exchanger, the temperature of the heated medium can be controlled. For example, there is a regulating valve before the heat source inlet, and changing the valve opening can adjust the outlet temperature.
The production process of
The design and manufacture of shell-and-tube heat exchangers is a complex process that requires comprehensive consideration of many factors, including process requirements, material selection, structural design, safety standards, etc.
1. Check the heat transfer coefficient and heat transfer area: Calculate the heat transfer coefficient K and heat transfer area F according to the heat transfer coefficient of pipe and shell, dirt thermal resistance, wall thermal resistance, etc. This step takes into account a number of factors, such as differences between operating conditions and design conditions, and possible future scaling or clogging problems.
2. Manufacturing technology: The manufacturing process of shell and tube heat exchanger includes selecting the appropriate material, determining the specifications and arrangement of the tube bundle, and the number of baffle or support plate. These manufacturing details are critical to the performance and durability of heat exchangers.
3. Design conditions: Users need to provide some key design conditions, such as operating pressure, operating temperature, metal wall temperature, material name and characteristics, corrosion margin, number of passes, heat exchange area, heat exchange tube specifications, etc. This information is essential for the design of an efficient and safe heat exchanger.
Production of equipment

Wteya aims to digital and intelligent production to provide superior products and services to its customers. We not only provide a wide range of standard products which are seriously tested and stable performance to meet a wide range of industrial needs. We also provide custom service, as well as OEM and ODM services, professional design team provides proper solutions for customers to meet their unique needs. We will work closely with each customer to ensure that every device suits customer's process requirements and production process accurately. Wteya's one-stop service, innovative to create high-quality mechanical products and system solutions, professionally help customer deal with various water treatment problems.
Capacity and size
|
Basic parameter table (outer diameter of heat exchange tube Ø20) |
||||||||
|
Nominal diameter |
Number of heat exchange tubes |
Center arrangement tube |
Pipe flow area |
Calculate the heat transfer area |
||||
|
1500 |
2000 |
3000 |
4500 |
6000 |
||||
|
159 |
15 |
5 |
0.003 |
1.4 |
1.9 |
2.8 |
|
|
|
219 |
33 |
7 |
0.0066 |
3.1 |
4.1 |
6.2 |
|
|
|
273 |
65 |
9 |
0.013 |
6.1 |
8.2 |
12.3 |
18.4 |
24.5 |
|
325 |
99 |
11 |
0.0199 |
9.3 |
12.4 |
18.7 |
28 |
37.3 |
|
400 |
174 |
14 |
0.035 |
16.4 |
21.9 |
32.8 |
49.2 |
65.6 |
|
500 |
275 |
19 |
0.0553 |
|
34.6 |
51.8 |
77.8 |
103.7 |
|
600 |
433 |
21 |
0.136 |
|
54.4 |
81.6 |
122.5 |
163.2 |
|
700 |
595 |
25 |
0.187 |
|
74.7 |
112.1 |
168.2 |
224.3 |
|
800 |
769 |
29 |
0.242 |
|
96.6 |
144.9 |
217.4 |
290 |
Frequently Asked Questions
Large fluctuation of outlet pressure: this may be caused by leakage at the connection between the tube and the tube plate. The sealing of the joint needs to be checked regularly, and the necessary maintenance and replacement are carried out.
Scaling problem: Scaling will affect the heat transfer efficiency, regular cleaning of the heat exchanger, the use of appropriate cleaning agents and methods to remove the inner wall of the scale, you can maintain the heat transfer efficiency.
Corrosion problems: Corrosion can compromise the life and safety of heat exchangers. Choosing corrosion-resistant materials to make heat exchangers, or adding inhibitors to corrosive media, can reduce the occurrence of corrosion.
Leakage problem: Leakage may be caused by poor sealing or damage to the bundle. Regular inspection of seal and tube bundle condition, timely replacement of damaged parts, can prevent leakage problems.







